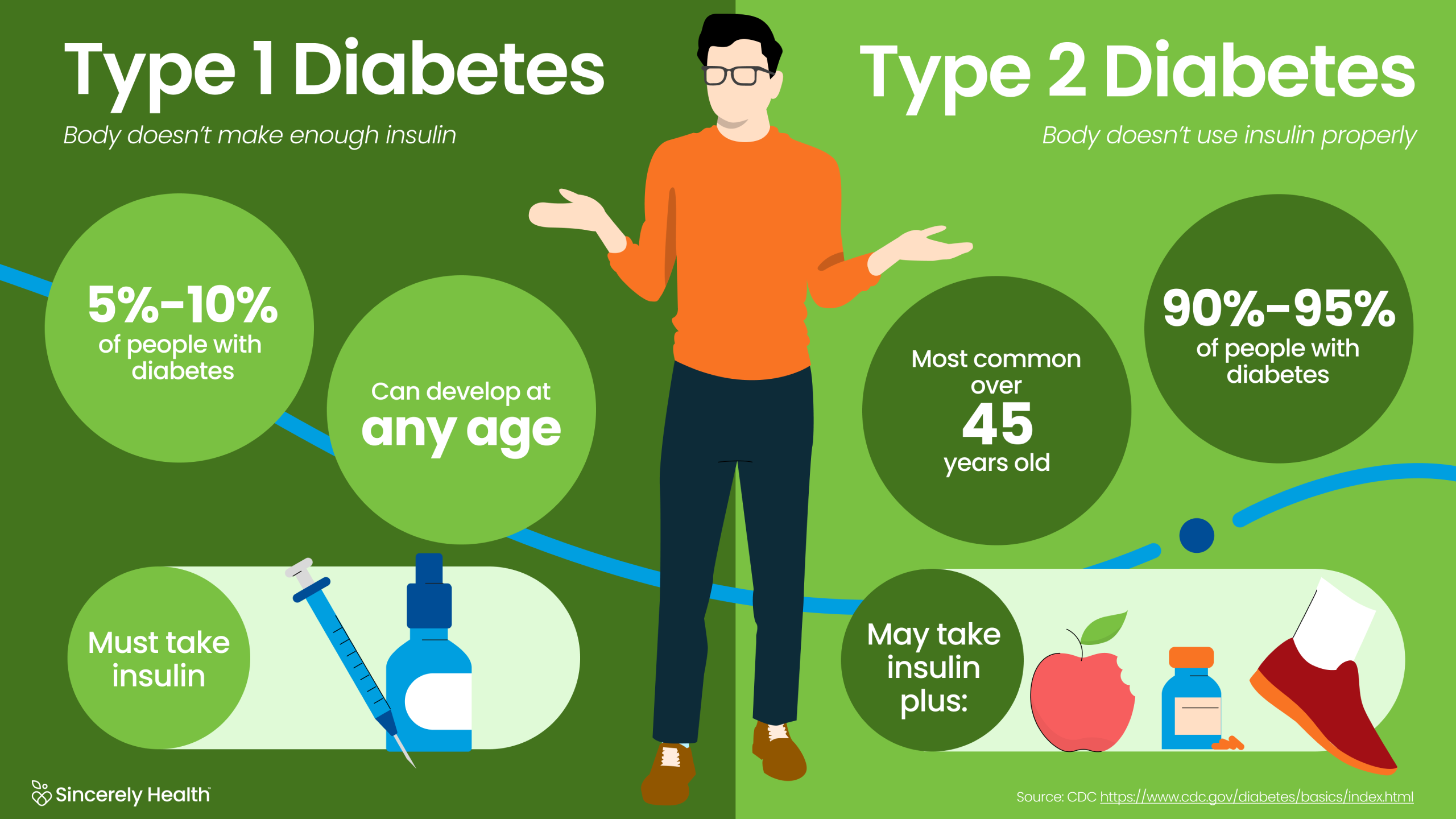
Type 1 and type 2 Diabetes facts
Type 1 diabetes, also called juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This condition prevents the body from producing insulin, a hormone essential for converting glucose into energy. While it can occur at any age, type 1 diabetes is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
The exact causes of type 1 diabetes remain unknown, but genetics and environmental factors are thought to play a significant role. Unlike type 2 diabetes, lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise do not influence the onset of type 1 diabetes.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurry vision. In severe cases, individuals may develop diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a potentially life-threatening condition caused by extremely high blood sugar levels.
Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes
Management of type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy. People with type 1 diabetes use insulin injections or insulin pumps to regulate blood sugar levels. Additionally, consistent monitoring of blood glucose and a well-balanced diet are crucial.
Exploring Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for more than 90% of cases worldwide. Unlike type 1, type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is influenced by several factors, including obesity, sedentary lifestyle, genetic predisposition, and age. High-calorie diets and a lack of physical activity significantly increase the risk.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop gradually and may go unnoticed for years. These include increased thirst, frequent urination, slow-healing sores, frequent infections, and numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
Management of type 2 diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Healthy eating, regular physical activity, and weight loss are the primary strategies for controlling blood sugar levels. Medications such as metformin, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors may be prescribed.
Key Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
While both types of diabetes share the common feature of elevated blood sugar levels, they differ significantly in causes, onset, and management.
- Onset Age: Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in younger individuals, whereas type 2 diabetes is more prevalent in adults over 40.
- Cause: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder, while type 2 diabetes is largely related to lifestyle and genetics.
- Insulin Dependence: People with type 1 diabetes require insulin for survival, while those with type 2 diabetes may not need insulin initially.
- Risk Factors: Type 1 diabetes is linked to genetic and environmental factors, whereas type 2 diabetes is closely tied to obesity and inactivity.
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
While type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, type 2 diabetes can often be delayed or avoided through lifestyle adjustments.
Healthy Eating
Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables is key. Avoiding sugary beverages and processed foods also helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week improves insulin sensitivity and promotes overall health.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of developing insulin resistance. Even modest weight loss can have significant benefits for those at high risk.
Monitoring and Early Intervention
Regular screenings for blood sugar levels, particularly for those with a family history of diabetes or other risk factors, can lead to early detection and intervention.
Living with Diabetes
For those diagnosed with either type of diabetes, self-care and education are vital to maintaining quality of life. This includes regular check-ups with healthcare providers, adhering to prescribed treatments, and staying informed about advancements in diabetes care. Support groups and counseling can also help individuals cope with the challenges of living with diabetes.
By understanding the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, individuals can take proactive steps toward prevention, effective management, and a healthier lifestyle.